What is CNC Cutting and How Does it Work?
CNC cutting has revolutionized the manufacturing industry. It offers precision and efficiency across various sectors. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global CNC cutting market is projected to reach $8.8 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 6.1%. This trend showcases the increasing reliance on CNC cutting technology.
CNC cutting refers to the computer-controlled process of cutting materials such as metal, wood, and plastics. It utilizes various methods, which include laser cutting, plasma cutting, and water jet cutting. Each method has its unique applications. For example, laser cutting provides clean edges and intricate designs. This versatility is appealing in industries ranging from automotive to aerospace.
Despite its advantages, CNC cutting still faces challenges. The initial setup costs can be high. Additionally, not all companies can afford the latest technology. This creates a gap between industry leaders and smaller businesses. As more companies adopt CNC cutting, the need for skilled technicians rises. Continuous training is essential to keep pace with evolving technology.
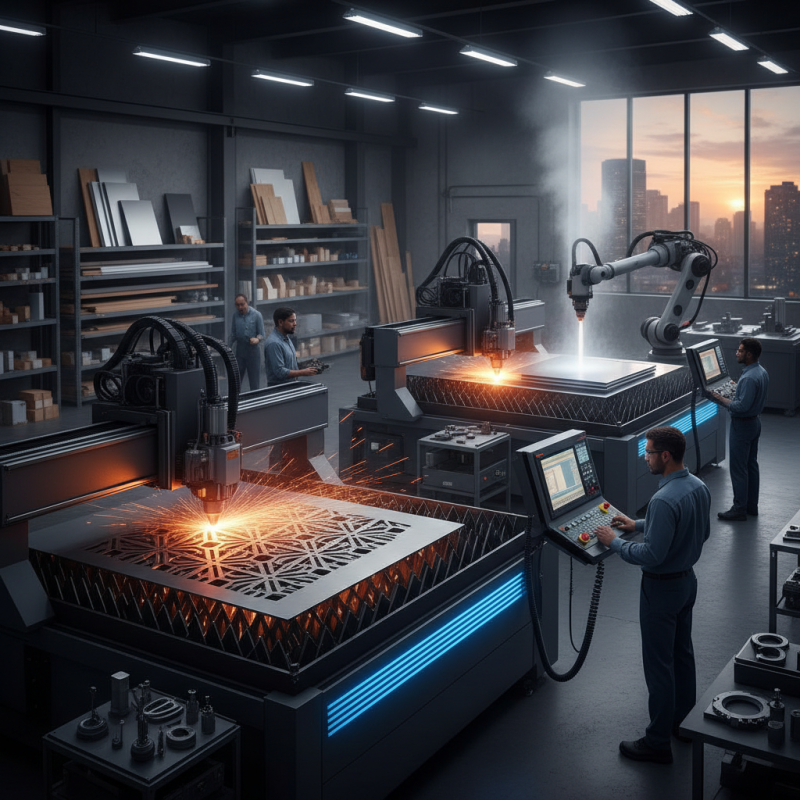

What is CNC Cutting?
CNC cutting stands for Computer Numerical Control cutting. It is a precise method of cutting materials using automated machines. The process involves translating a computer-aided design (CAD) into a set of commands. These commands tell the CNC machine how to move and operate.
According to a 2021 industry report, the CNC market is projected to reach $117 billion by 2027. This growth highlights the rising demand for precision manufacturing. Companies often prefer CNC cutting for its accuracy and efficiency. Yet, challenges remain. Maintaining the machines requires skilled personnel. Many small businesses struggle with the costs associated with high-quality CNC equipment.
CNC cutting can be applied to various materials. These include wood, metal, and plastics. However, operators must understand the limitations of their machines. Misalignment or incorrect programming can lead to waste. This can frustrate manufacturers aiming for productivity. Ensuring rigorous training for operators can mitigate errors, but it is not always prioritized in every shop. Production efficiency needs constant attention.
The History and Evolution of CNC Technology
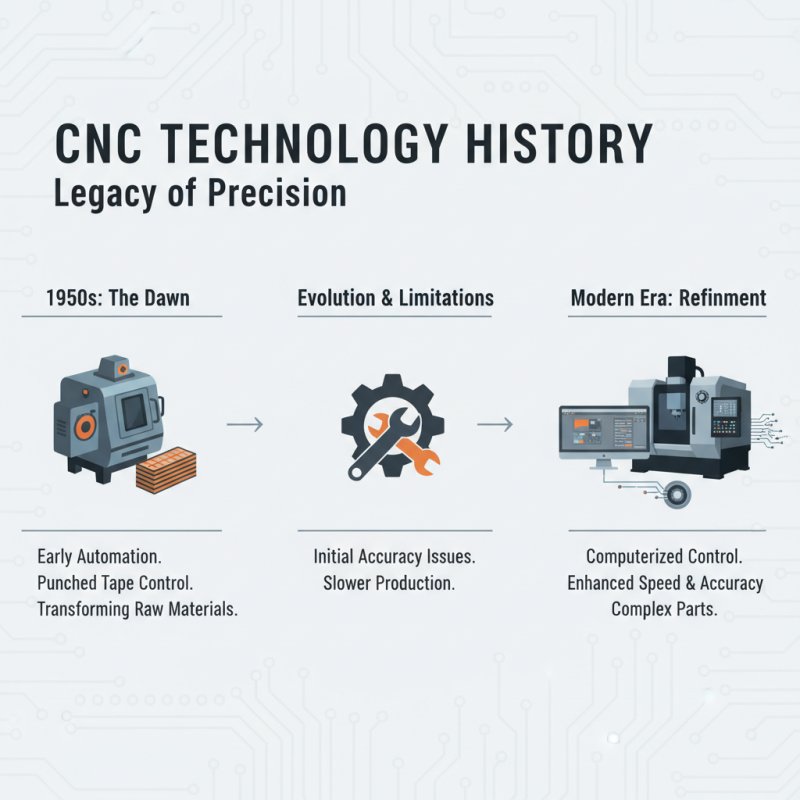
The history of CNC technology dates back to the 1950s. It began as a way to automate machining processes. Early systems used punched tape to control machines. These machines transformed raw materials into precise parts. However, limitations existed. The accuracy and speed were not optimal.
In the 1970s, computer technology improved. This advancement led to the development of more sophisticated CNC systems. They allowed for complex geometries and faster production times. Still, operators faced a learning curve. Understanding the programming was not intuitive for everyone. Over the years, as tools evolved, user interfaces became more friendly. But some machines still required extensive training.
Today, CNC technology is a staple in manufacturing. It is found in various industries, from aerospace to furniture. Yet, the technology is not perfect. Some machines remain underutilized due to lack of skilled operators. There are ongoing debates about the impact of CNC on traditional craftsmanship. As CNC continues to evolve, the balance between technology and human skill remains a poignant issue.
How CNC Cutting Machines Operate
CNC cutting machines are powerful tools used in various industries. They operate using computer numerical control technology. This means that a computer program directs the actions of the cutting tool. The precision of this method is impressive. Cuts are accurate, often within a thousandth of an inch. However, not every design translates perfectly into reality.
The machines use different cutting methods. Some use lasers, while others utilize water jets or plasma. Each method has its pros and cons. For instance, laser cutting creates clean edges but can generate heat distortion. Water jet cutting avoids heat but may require more cleanup. Operators must understand these nuances. Small errors can lead to significant material waste.
Software plays a critical role in CNC cutting. It converts design files into machine-readable instructions. If the software malfunctions or the design is flawed, issues may arise. Users may need to test different settings for optimal results. Adapting to the intricacies of each process takes time and patience. Mistakes are part of learning in this field.
Key Components of CNC Cutting Systems
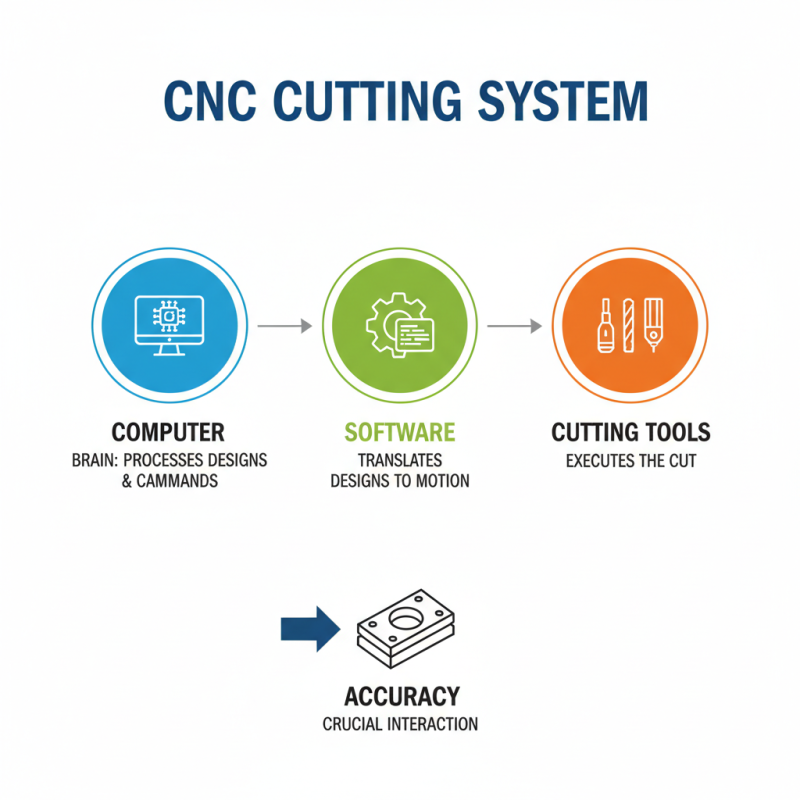
CNC cutting systems consist of several key components. These include the computer, software, and cutting tools. The computer serves as the brain of the operation. It processes design files and sends commands to the machine. Software translates design concepts into precise movements. The interaction between these elements is crucial for accuracy.
Cutting tools play a significant role in CNC cutting. They vary depending on the material being cut, such as metal or wood. Some tools are designed for specific tasks, like engraving or milling. It’s important to choose the right tool for the job. An incorrect choice can lead to poor results. Over time, tools may wear out, necessitating regular inspection and replacement.
Another component is the motion system. This system allows the cutting head to move in different directions. It often includes motors and rail systems. The calibration of these systems affects the final product. If aligned incorrectly, issues can arise. Regular maintenance is necessary to ensure optimal performance. This involves cleaning, checking alignment, and updating components as needed.
Applications and Industries Utilizing CNC Cutting
CNC cutting is widely used in various industries. Its precision and efficiency make it a top choice for manufacturing. The automotive sector benefits greatly from this technology. Parts need to be cut accurately to ensure safety and performance. CNC machines can handle complex shapes and designs. This capability saves time and reduces waste.
The construction industry also utilizes CNC cutting. Panels and beams are fabricated with high precision. This leads to better fitting and stronger structures. Moreover, the aerospace sector relies heavily on CNC cutting. Components must be lightweight yet strong. Precision cutting helps achieve this balance.
However, not every application is perfect. Some industries face challenges in adapting to CNC technology. Training staff can be a hurdle. Updates in software and equipment also require time and investment. Reflecting on these issues can drive improvement. Understanding the limitations is just as important as harnessing the benefits.
Related Posts
-

Revolutionizing Precision: How CNC Cutting is Transforming Modern Manufacturing Processes
-

The Definitive Ultimate Guide to Mastering CNC Cutting Techniques for Precision Fabrication
-

Common Issues Faced in CNC Cutting Operations
-

Exploring CNC Cutting Innovations at the 138th Canton Fair 2025 in China
-

How to Use CNC Cutting Techniques for Precision Fabrication in 2025
-

Ultimate Guide to Mastering CNC Turning Techniques for Precision Engineering